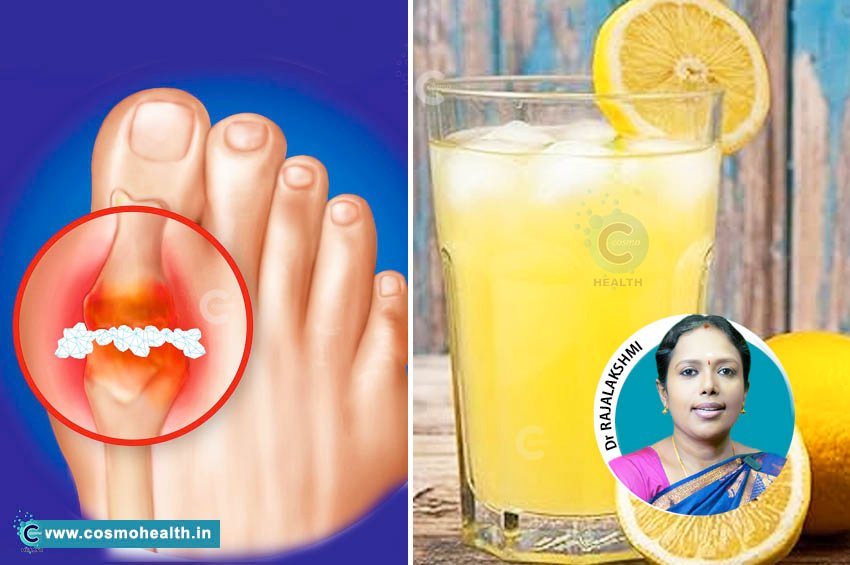
Managing uric acid levels is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health, especially for individuals prone to joint pains and related conditions. High uric acid levels can lead to several health issues, including gout and kidney stones. In this article, we will delve into the causes of high uric acid, the consequences it can have on the body, and effective strategies to lower these levels for improved health.
Uric acid is a natural waste product created when the body breaks down purines, substances found in various foods. Under normal circumstances, uric acid is dissolved in the blood, filtered by the kidneys, and then excreted through urine. However, when there's an excess of uric acid, it can build up in the body, leading to conditions such as gout—a form of arthritis characterized by painful swelling in the joints.
Causes of High Uric Acid
High levels of uric acid, known as hyperuricemia, can result from several factors:
- Dietary Factors: Foods rich in purines, like red meat and certain seafood, can significantly increase uric acid levels. Additionally, beverages high in sugar and alcohol consumption, particularly beer, can exacerbate the issue.
- Obesity: Being overweight can lead to an increase in uric acid production and a decrease in its excretion.
- Medication: Certain diuretics and medications used in chemotherapy can lead to elevated uric acid levels.
- Kidney Health: Impaired kidney function can prevent the proper excretion of uric acid, causing it to accumulate in the body.
Effects of High Uric Acid on Health
High uric acid levels can manifest in various ways, most notably:
- Gout: Acute attacks usually present with sudden, severe pain in the joints, often affecting the big toe.
- Kidney Stones: Uric acid can crystallize in the kidneys, forming stones that can cause intense pain and complications.
- Kidney Disease: Chronic high levels can lead to kidney damage over time.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Some studies suggest a link between high uric acid levels and increased cardiovascular risks.
Effective Strategies to Lower Uric Acid
Lowering uric acid levels involves a combination of dietary changes, hydration, and lifestyle adjustments:
1. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for flushing out uric acid from the body. Aim for at least 4–5 liters of water daily to help maintain normal uric acid levels.
2. Dietary Alterations
- Reduce Purine-Rich Foods: Limit intake of red meats, organ meats, and certain types of fish.
- Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Opt for foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits (berries, apples), vegetables (spinach, kale), and whole grains.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in fiber can aid digestion and help lower uric acid levels.
- Choose Low-Fat or Non-Dairy Products: These can provide protein without the high levels of purine found in meats.
- Include Lemons and Citrusy Fruits: Lemons are particularly beneficial as the citric acid helps reduce uric acid levels.
3. Natural Remedies
Incorporating specific drinks into your daily routine can aid in lowering uric acid:
- Lemon Juice in Warm Water: Mix the juice of half a lemon in warm water and drink it first thing in the morning.
- Baking Soda: Mixing half a teaspoon of baking soda in water can act as a quick solution for alleviating pain and potentially lowering uric acid levels. However, consult with a healthcare provider before regular use, especially if you have kidney issues.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, green tea can support overall health and potentially lower uric acid levels.
4. Monitor Your Meat and Seafood Intake
Be cautious with meat and seafood and consider replacing a portion of your protein sources with plant-based options. Fish is typically lower in purine than most red meats, which makes it a preferred choice if moderation is adhered to.
5. Regular Check-ups
Regular blood tests to monitor uric acid levels are essential for individuals prone to hyperuricemia. This can help in making timely interventions and adjustments in diet or medication where necessary.
Conclusion
High uric acid levels pose significant health risks, especially concerning joint health and kidney function. Understanding the causes and implementing effective strategies can help manage and lower uric acid levels effectively.
Adopting a balanced diet, maintaining hydration, and leading a healthier lifestyle are key components in this journey. Don’t wait until symptoms worsen; proactively manage your health and consider consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
By prioritizing your health and making these changes today, you can alleviate discomfort and contribute to long-term wellness. Embrace these strategies and take charge of your health now!