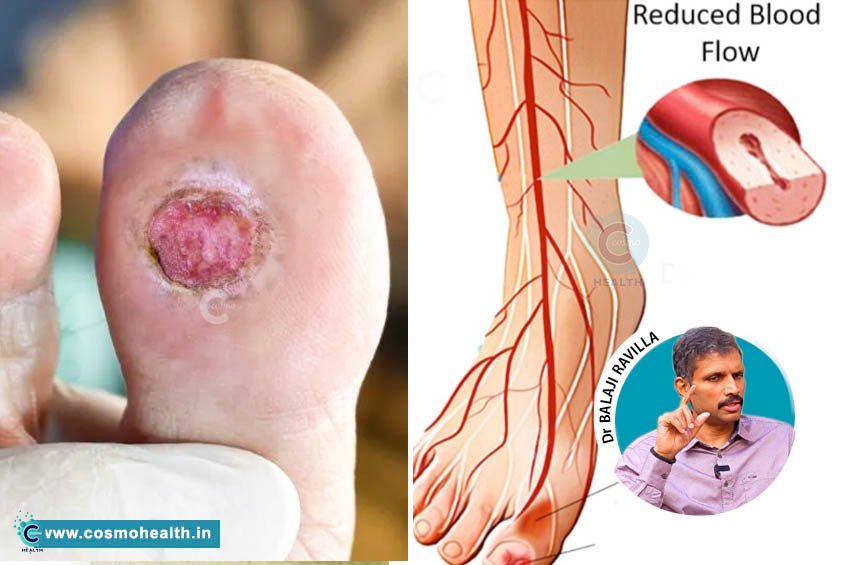
Diabetes is a complex and increasingly prevalent condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. One of the often-overlooked complications associated with diabetes is the development of foot ulcers. These painful wounds can lead to serious health issues, including infections and even amputations if left untreated.
In this article, we will delve deep into the topic of diabetic foot ulcers, exploring their symptoms, risk factors, treatment options, and preventive measures to help manage this condition effectively.
What are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that occur on the feet of individuals with diabetes, typically stemming from a combination of neuropathy and poor circulation. The condition is often linked to prolonged periods of high blood sugar levels that lead to nerve damage and reduced blood flow to the extremities.
Symptoms of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Persistent Foot Pain: Recurrent pain or discomfort in the feet, often increasing with worsening conditions.
- Skin Changes: Color changes, swelling, or the development of new sores or wounds on the feet.
- Loss of Sensation: Many individuals with diabetic neuropathy may not feel injuries, making them unaware of emerging ulcers until they escalate.
- Infections: Notable symptoms of infection may include redness, warmth, and drainage from the ulcer site.
Why Do They Occur?
Diabetic foot ulcers occur for several reasons:
- Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to loss of sensation and increasing the risk of injuries going unnoticed.
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes can impair blood flow, making it difficult for wounds to heal and increasing vulnerability to infections.
- Infection Risk: Once an ulcer develops, the risk of infection rises due to decreased immune response in diabetic individuals.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Poorly Controlled Blood Sugar Levels: Individuals with fluctuating or high blood glucose are at higher risk.
- Previous Foot Ulcers or Amputations: History of foot problems significantly increases the risk of recurrence.
- Foot Deformities: Structural changes in the foot can lead to increased pressure points and the likelihood of injuries.
- Smoking: Tobacco use contributes to circulation issues and increases the risk of developing ulcers.
Understanding the Stages of Wound Healing
Wound healing comprises several distinct stages, including hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Understanding these phases can aid diabetic patients and caregivers in monitoring their ulcers effectively:
- Hemostasis: The process where the body stops the bleeding by clot formation.
- Inflammation: Redness and swelling occur as the body begins to fight infection.
- Proliferation: New tissue begins to develop, and healing progresses.
- Remodeling: The final phase, where the skin strengthens.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
1. Medical Management
- Debridement: Regular removal of dead tissue to encourage healing.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for patients showing signs of infection.
- Advanced Dressings: Specialized dressings can promote a moist wound environment to facilitate healing.
2. Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue or even amputate compromised areas of feet. Timely surgical intervention can prevent the spread of infection and improve the chances of recovery.
3. Improving Blood Glucose Control
Achieving better control over blood sugar levels can significantly reduce the risk of developing ulcers and enhance healing for existing wounds. Patients should regularly monitor their blood sugar and follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Preventive Measures
1. Regular Foot Inspection
Daily foot checks can help catch any injuries before they become ulcers. Look for:
- Cuts, bruises, or sores.
- Redness or swelling.
- Changes in skin temperature or texture.
2. Proper Footwear
Wearing well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support can prevent injuries. Consider special diabetic footwear designed to reduce pressure on sensitive areas.
3. Promoting Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Managing weight, eating a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and staying active can significantly affect overall health and reduce complications from diabetes.
4. Regular Medical Check-ups
Routine appointments with healthcare providers can help manage diabetes and catch complications early. Health professionals can provide personalized advice and treatments tailored to individual needs.
Diabetic foot ulcers present serious health risks that can lead to significant complications if not managed effectively. Early detection and treatment are critical in preventing the progression of these ulcers. Individuals with diabetes should prioritize foot health, monitor their blood glucose levels, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals to maintain a high quality of life. Educating oneself about diabetic foot care is essential for prevention and successful management.
To learn more about how to effectively manage diabetes and prevent complications, consider reaching out to healthcare providers for personalized advice and treatment plans.